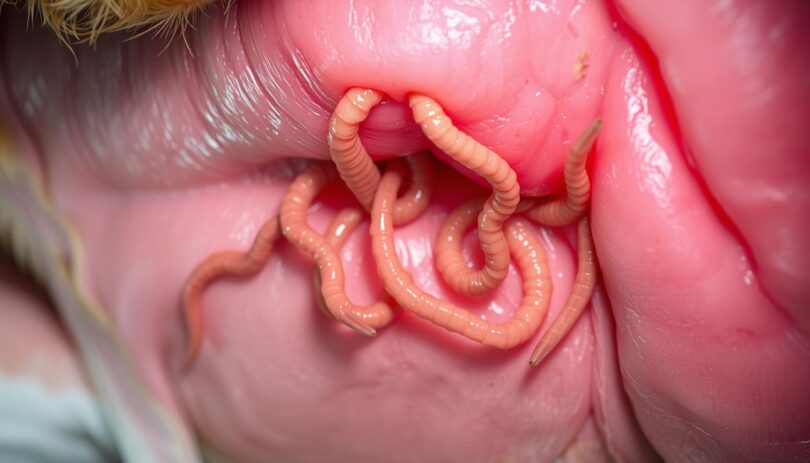
Hookworms are a common and dangerous intestinal parasite that can cause significant health issues in dogs. These tiny worms attach to the intestinal wall, leading to blood loss and anemia. If left untreated, hookworm infections can be life-threatening, especially for puppies.
Hookworm larvae can infect dogs through their skin or by ingesting contaminated soil. Puppies are particularly vulnerable, as they can become infected while nursing. Symptoms of hookworm infection include pale gums, diarrhea, and weakness. In severe cases, dogs may require hospitalization and blood transfusions.
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications. Veterinarians typically recommend broad-spectrum deworming medications, with follow-up treatments in two to three weeks. Regular fecal flotation tests are crucial for early detection and ensuring the infection is fully cleared.
Prevention is key to protecting your dog from hookworms. Monthly parasite prevention medications and good hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of infection. By understanding the signs and taking proactive steps, you can help keep your dog healthy and thriving.
Understanding Hookworm Infections in Dogs
Hookworms are intestinal parasites that pose serious health risks to dogs. These parasites can infect dogs through skin contact or by ingesting contaminated soil. Puppies are especially vulnerable, as they can contract the infection even before birth or through their mother's milk.
Lifestyle and Transmission Dynamics
Dogs can pick up hookworm larvae in contaminated environments. These larvae can penetrate the skin or be ingested, leading to infection. The parasite's lifecycle is about two to three weeks, during which they mature and start producing eggs. This cycle highlights the importance of regular fecal flotation tests for early detection.
Environmental Risk Factors and Vulnerable Populations
Warm, moist soil and crowded living conditions increase the risk of hookworm infection. Puppies, stray dogs, and dogs in crowded areas are more susceptible. Hookworms cause anemia due to their blood-feeding nature, which can be severe in young puppies. Preventive measures like monthly medications and good hygiene are crucial in reducing the risk of infection.
For more detailed information on diagnosing and treating hookworm infections, visit VCA Hospitals.
Recognizing Symptoms and Diagnosing Hookworm Infections
Hookworm infections can be challenging to detect in their early stages, but recognizing the signs is crucial for timely intervention. Both puppies and adult dogs may exhibit visible symptoms that indicate the presence of these parasites.
Visible Signs in Puppies and Adult Dogs
One of the most noticeable signs of a hookworm infection is pale gums, which result from the parasite feeding on the dog's blood. Puppies and adult dogs may also experience weakness and noticeable weight loss. These symptoms can develop gradually, making it essential to monitor your dog's health closely.
Diagnostic Methods: Fecal Flotation and Beyond
Diagnosing hookworm infections typically involves a fecal flotation test, which detects the parasite's eggs in the dog's stool. This method is effective because hookworms produce a large number of eggs daily. However, because the worms are microscopic, they may not be visible in stool samples, making laboratory testing necessary.
Timing and Veterinary Consultation
It's crucial to consult a veterinarian promptly if you notice any symptoms, as early detection can prevent severe outcomes. Repeat testing is often recommended 2-3 weeks after initial treatment to ensure that all larvae have been eliminated. Understanding the connection between clinical signs, such as diarrhea and anemia, and hookworm infection is key to effective management.
Effective Treatment and Prevention for hookworms in dogs
Effective treatment and prevention of hookworm infections in dogs require a combination of medication and good hygiene practices. Veterinarians often recommend anthelmintic medications, such as pyrantel and fenbendazole, which are effective against hookworm larvae and adult worms.
Anthelmintic Medications and Treatment Intervals
These medications work by targeting the parasites in the intestines, ensuring that both adult worms and larvae are eliminated. It’s crucial to follow the recommended treatment schedule, which typically includes an initial dose followed by a second treatment two to three weeks later. This ensures that any larvae that were not affected by the first dose are eliminated, as they may have been in a stage not susceptible to the medication at the time of the first treatment.
Home Care: Managing the Environment and Diet
Home care plays a vital role in preventing re-infestation. Regular cleaning of your dog’s bedding and prompt removal of feces from your yard or public spaces can significantly reduce the risk of hookworm larvae surviving in the environment. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports your dog’s recovery and overall intestinal health during treatment.
Environmental factors, such as soil contamination, should also be controlled. Hookworm larvae thrive in warm, moist soil, so keeping your yard clean and disposing of waste properly can help break the parasite’s lifecycle. For more information on managing gastrointestinal health, visit this resource for expert advice.
By combining professional veterinary care with proactive home management, you can effectively treat and prevent hookworm infections, ensuring your dog remains healthy and thriving.
Essential Steps for Long-Term Canine Health and Parasite Control
Maintaining your dog's health requires a proactive approach to parasite control. Regular veterinary check-ups and stool tests are vital to ensure hookworm infections are fully treated and prevented from recurring.
Year-round prevention programs, including monthly medications that target both hookworms and heartworms, are highly effective. These medications not only protect your dog but also contribute to preventing the spread of parasites in the environment.
Keeping your dog's living space clean is another crucial step. Prompt removal of feces and regular cleaning of bedding can significantly reduce the risk of larvae survival. Additionally, avoiding contaminated areas helps prevent reinfection.
Vigilance is key. If you notice any signs of infection, such as pale gums or weight loss, contact your vet immediately. Early action can prevent complications and ensure your dog's well-being.
By combining professional veterinary care with consistent home maintenance, you can create a healthy environment for your dog. This balanced approach reduces the risk of hookworm infections and supports long-term health.
FAQ
Why are young puppies more susceptible to hookworm infections?
Young puppies have underdeveloped immune systems and can become infected through their mother's milk. They are also more vulnerable to the effects of anemia and weight loss caused by hookworms.
How long does it take to treat a hookworm infection in dogs?
Treatment typically takes a few weeks, depending on the severity of the infection. Your vet may recommend multiple doses of medication to ensure all larvae and adult worms are eliminated.
Can I use over-the-counter medications to treat hookworms in my dog?
It's best to use medications prescribed by a vet, as they are more effective and safer for your dog. Over-the-counter products may not fully eliminate the infection and could have side effects.
How can I protect my environment from hookworm contamination?
Regularly clean up your dog's stool, dispose of waste properly, and treat your dog with preventive medications. Keeping your yard clean can reduce the risk of hookworm larvae in the soil.









Leave a Comment